Intelligent automation is the combination of artificial intelligence (AI) and robotic process automation (RPA) that is used to create smart business processes and workflows that think, learn, and make decisions on their own.
It represents an evolved stage of automation in which machines mimic human actions and possess cognitive capabilities, including machine vision, natural language generation (NLG), speech recognition, and machine learning (ML). Such kind of machines with automated intelligence can be used to automate processes to acquire more operational and business effectiveness by assimilating vast amounts of structured and unstructured data, analysing, comprehending and learning the patterns.
This may involve processing millions of documents and applications a day, identifying and resolving issues within each, and synthesizing improvement recommendations. The concept of automation in the digital world is evolving, and technology is progressing by adding more capabilities of the human thought process into machines each day.
Different from Robotic Process Automation
RPA is the ability of a machine or software to perform a pre-programmed task repetitively, whereas Artificial Intelligence (AI) is nothing but the “intelligence” exhibited by a non-human entity.
According to IEEE Standards Association, RPA refers to the use of a “preconfigured software instance that uses business rules and predefined activity choreography to complete the autonomous execution of a combination of processes, activities, transactions, and tasks in one or more unrelated software systems to deliver a result or service with human exception management.”
And AI is “the combination of cognitive automation, machine learning (ML), reasoning, hypothesis generation and analysis, natural language processing and intentional algorithm mutation producing insights and analytics at or above human capability.”
On the most rudimentary level, RPA is related to “doing” whereas AI and ML are concerned about “thinking” and “learning” separately.
Intelligent Automation is simply the amalgamation of the above.
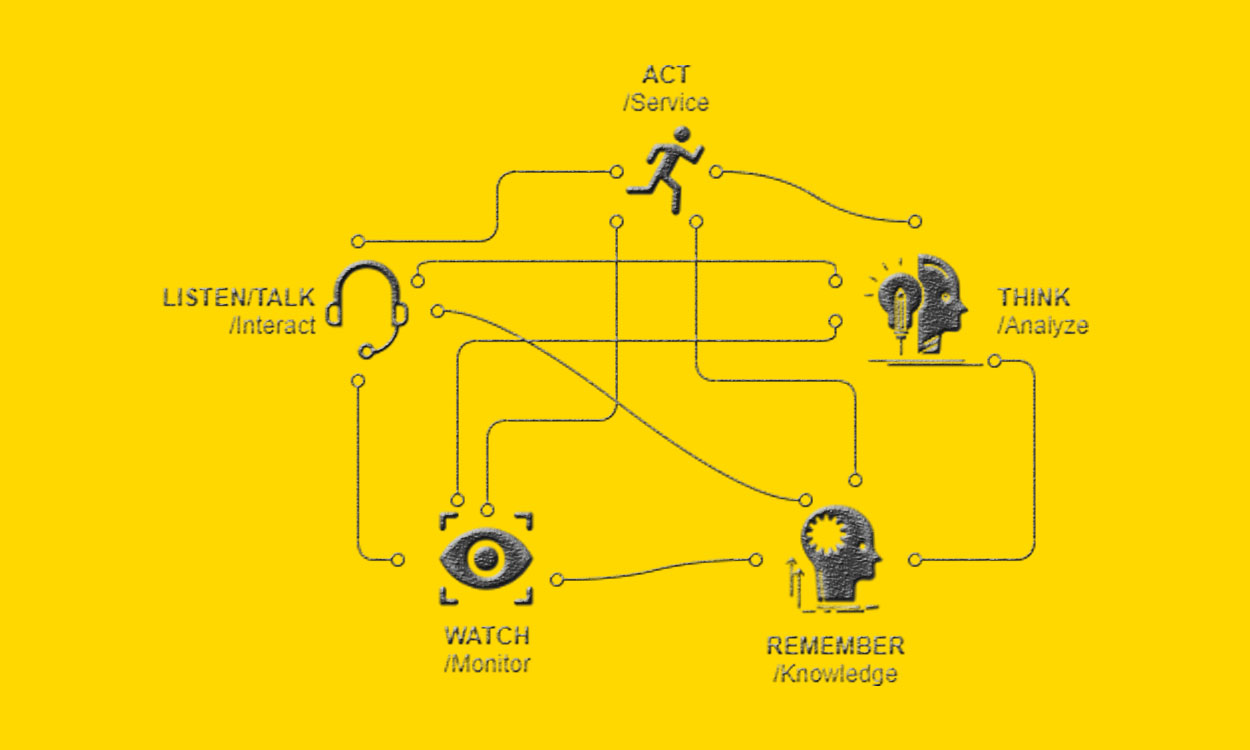
The Five Senses of Intelligent Automation
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): a software automation tool that is used by organizations to automate tasks that were previously done by human beings across applications and systems. This helps in saving time and manpower. Daily manual tasks such as information extraction and cleaning through user interfaces that are already there in the system can be automated. The robot is assigned a User ID and it can perform tasks such as accessing and extracting email contents, executing calculations, generating reports, and checking files based on predefined conditions.
Workflow Processor: a process-management software system tool that consolidates tasks performed by groups of humans and machines where the human’s task is to manage the robot. Using this tool, the users can track the complete end-to-end process in real-time and the software system can look over the handoff between different teams like robots and human users and provide statistical data in case of hold-up.
Machine Learning: algorithms that can learn from data, derive and identify patterns in structured data through supervised and unsupervised learning techniques, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. Supervised algorithms learn from labeled data sets of inputs and outputs and then provide the predictions on the new inputs. Unsupervised algorithms try to learn by extracting features and patterns on its own using unlabelled data. Machine learning and advanced analytics could be a game-changer for the insurance industry as it can help in claims processing, insurance advise, prevent fraud, reduce cost structures and can help in risk management. It can also derive insights from the data which will help the company gain a competitive advantage.
Natural-language Generation (NLG): a software process that can automatically translate observations from data into a language people use for reading and writing by following rules. As NLG helps us converse with the system that has access to our data, the interaction becomes much more natural. There’s a difference between getting a report and having a conversation and NLG helps us fill the gap between those two. Internal and External management reports can be generated automatically by using structured performance data as an input for natural language.
Cognitive Agents: a powerful agent that can handle time-consuming manual tasks and free up human resources to tackle more complex tasks. Cognitive agents are built by combining machine learning and natural-language generation and is capable of mimicking the human brain by using data mining, pattern recognition and Natural Language Processing. It can execute tasks, communicate, learn from data sets and can identify and extract contextual elements. Cognitive agents can be utilized to help workers and clients via telephone or via chat, for example, in representative assistance places.
Future Prospects
Intelligent Automation connects humans, business processes, and technologies to augment business growth, drive revenue, reduce costs, mitigate risk, and deliver an exceptional user experience.
The vital benefit of utilizing an Intelligent Automation arrangement is that one can accomplish straight-through processing (with minimal human mediation). The disadvantages are expanded expenses and process intricacies.
With Intelligent Automation, progressive organizations are already relocating advanced operational and cognitive processes to machines – solving complex business problems at a rapid rate, far beyond that of human beings, thereby enhancing productivity, quality, predictability, and agility while decreasing time to market – at a reduced cost to the business.
The author is Head — IT, Hannover Re – India Branch. Views are personal.
